CAN interface: CAN is the abbreviation of Controller Area Network (CAN). It was developed by the German BOSCH company,
which is known for its research and development and production of automotive electronic products, and eventually became an
international standard (ISO 11898). One of the most widely used fieldbuses. In North America and Western Europe, the CAN bus protocol has become the standard bus for automotive computer control systems and embedded industrial control local area networks, and has the J1939 protocol designed specifically for large trucks and heavy machinery vehicles with CAN as the underlying protocol.
OBD system: The full name of OBD: On Board Diagnostics is translated into Chinese as: is a detection system extended for automobile fault diagnosis. "OBD Ⅱ" is "on Board Diagnostics Ⅱ", the abbreviation of Type Ⅱ on-board diagnostic system.
In order to standardize the diagnosis of vehicle emission and drive-related faults, starting from 1996, all new vehicles sold in the United States must have similar diagnostic equipment, fault codes and maintenance procedures, that is, complying with OBD II procedures.
With the increasing degree of economic globalization and automobile internationalization, the OBD Ⅱ system will be more and more widely implemented and applied as the basis for driving and emission diagnosis. The OBD Ⅱ program makes automobile fault diagnosis simple and uniform, and maintenance personnel do not need to learn new systems from each manufacturer.
Pixels: Pixels are composed of small squares of an image. These small squares have a clear position and assigned color value. The color and position of the small squares determine the appearance of the image.
You can think of a pixel as an indivisible unit or element in the entire image. Indivisible means that it can no longer be cut into smaller units or elements. It exists as a small grid with a single color. Each dot matrix image contains a certain amount of pixels, which determine the size of the image on the screen.
Resolution (display resolution and image resolution): Resolution, also known as resolution and definition, can be subdivided into display resolution, image resolution, printing resolution, and scanning resolution.
Data Rate: The code stream (Data Rate) refers to the number of changes in the high and low levels of the communication port during data transmission within 1 second. It is also called the code rate.
The more data transmitted per unit time, the more information it contains. The more is the most important part of picture quality control in video coding.
Canbus: As the ISO11898CAN standard, CANBus (ControLLer Area Net-work Bus) is a serial bus system for connecting field devices (sensors, actuators, controllers, etc.) and broadcasting-oriented in manufacturing plants. ) Developed for use in the automotive industry, and then increasingly appear in the manufacturing automation industry.
The CANBus system connects industrial equipment (such as limit switches, photoelectric sensors, pipeline valves, motor starters, process sensors, frequency converters, display boards, PLCs and PCI workstations, etc.) through corresponding CAN interfaces to form a low-cost network.
AHD/HD-SDI/HD-CVI/HD-TVI:
1. AHD: Analog High Definition means analog high resolution. Regarding High Definition, in simple terms, we usually call the format with a physical resolution of 720p or higher as HD, or HD for short. It refers to the vertical resolution of the screen. 1080i, 720p, or 1080p. 1080i means that the resolution is 1920×1080, and it uses interlaced scanning to present 30 complete pictures per second; 720p refers to the resolution of 1280×720, which uses sequential progressive scanning, and presents 60 complete pictures per second; 1080p refers to the resolution of 1920×1080, which adopts sequential scanning and presents 60 complete pictures per second. AHD is based on the AHD protocol and uses an analog coaxial cable to transmit progressively scanned high-definition video.
2. HD-SDI (serial digital interface) is the "digital component serial interface". Then, HD-SDI is a high-definition digital component serial interface. HD-SDI is a real-time uncompressed high-definition broadcast and television camera. It is another technological advancement in the field of security surveillance, and it is a device that provides a high-definition image source for the surveillance center.
3. HD-CVI: HDCVI (High Definition Composite Video Interface), the high-definition composite video interface, is a high-definition video transmission specification based on coaxial cable, which uses analog modulation technology to transmit progressively scanned high-definition video.
The HDCVI high-definition composite video interface standard has completely independent intellectual property rights. The first draft of its white paper version 0.50 was released by Zhejiang Dahua Technology Co., Ltd. on July 31, 2012. The latest version is version 1.00,
which was released on November 15, 2012. Officially released.
4. HD-TVI: HD-TVI is the coaxial high-definition video transmission standard. It is a high-definition video transmission specification based on coaxial cable. As a new analog high-definition solution, it can make up for the defect of the existing analog high-definition video in the market.
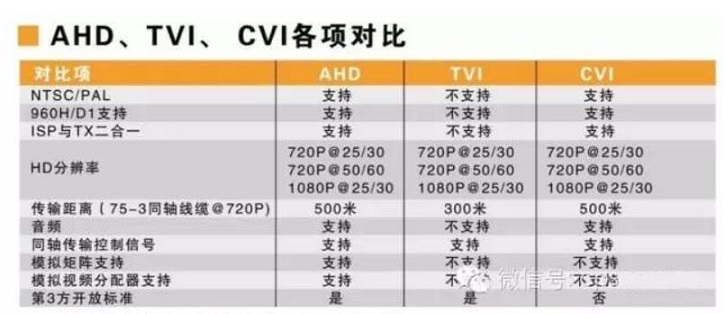
Comparison of AHD, TVI and CVI:
 4G module:
4G module: The 4G module refers to a product in which the hardware is loaded into the specified frequency band, the software supports the standard LTE protocol, and the software and hardware are highly integrated and modularized. The hardware integrates radio frequency and baseband on the PCB board to complete wireless reception, transmission, and baseband signal processing functions. The software supports functions such as voice dialing, SMS sending and receiving, and dial-up networking. It has the characteristics of good compatibility, large amount of communication data and fast speed. The 4G module supports FDD LTE/TD-LTE two LTE standards, and is also backward compatible with 2G/3G, and supports LTE-FDD, LET-TDD, WCDMA, TD-SCDMA, CDMA, GSM and other frequency bands.
GPS module: GPS module is an integrated circuit that integrates RF radio frequency chip, baseband chip and core CPU, plus related peripheral circuits. At present, most of the GPS chips of GPS modules are based on the SiRFIII series, which has the world's largest market share. Because GPS modules use different chipsets, performance and price are also different. GPS modules using SIRF third-generation chipsets have the best performance, and their prices are much more expensive than those using GPS chipsets such as MTK or MSTAR. At this stage, the chip is also being upgraded continuously, such as sirf4 and then sirf5. The overall sensitivity has been improved a lot, shortening the positioning time, and also helping customers quickly enter the positioning application state.
BeiDou Module: BeiDou is the abbreviation for Chinese BeiDou Navigation Satellite System (BeiDou Navigation Satellite System, referred to as BDS), a global satellite navigation system developed by China and the third mature satellite navigation system after GPS and GLONASS. Beidou Satellite Navigation System (BDS), American GPS, Russian GLONASS, EU GALILEO, are the suppliers that have been recognized by the United Nations Satellite Navigation Commission. The Beidou satellite navigation system is composed of three parts: space segment, ground segment and user segment. It can provide high-precision, high-reliability positioning, navigation, and timing services for all kinds of users around the world, all-weather and all-day, and it has short message communication capabilities, with preliminary capabilities of regional navigation, positioning, and timing. The positioning accuracy is in decimeter and centimeter level, the speed measurement accuracy is 0.2 m/s, and the timing accuracy is 10 nanoseconds.
GLONASS module: GLONASS, which is the abbreviation of "GLOBAL NAVIGATION SATELLITE SYSTEM" in Russian. The function of the GLONASS satellite navigation system is similar to the GPS of the United States, the Galileo satellite positioning system of Europe and the Beidou satellite navigation system of China. The system was first developed in the Soviet Union, and the program was continued by Russia. Russia began to independently establish its own global satellite navigation system in 1993. The system began operations in 2007, when only satellite positioning and navigation services in Russia were opened. By 2009, its service scope has expanded to the world. The main service content of the system includes determining the coordinates and moving speed information of land, sea and air targets. The "GLONASS" navigation system currently has 30 satellites in orbit, and the Russian space agency plans to launch three more in 2014. On November 11, 2014, it was reported that “Russian Space Systems” announced that the company is ready to deploy the Russian satellite navigation system GLONASS differential correction and monitoring system station (SDCM) in China. The installation work will be carried out in the month of December. NV08C-CSM, as the industry's leading wireless module supplier, SIMCom Unlimited Technology Co., Ltd. ("SIMCom"), today launched a new module that supports GPS, Galileo, QZSS and GLONASS satellite navigation systems, SIM68.
WiFi module: Wi-Fi module, also known as serial port Wi-Fi module, belongs to the transmission layer of the Internet of Things. Its function is to convert the serial port or TTL level to an embedded module that conforms to the Wi-Fi wireless network communication standard. It has a built-in wireless network protocol IEEE802. 11b.gn protocol stack and TCP/IP protocol stack.
Traditional hardware devices embedded in Wi-Fi modules can directly use Wi-Fi to connect to the Internet. It is an important part of realizing wireless smart home, M2M and other Internet of Things applications, and is an important part of smart hardware.
G-sensor: Gravity-Sensor, Acceleration Transducer, acceleration sensor is a sensor that can measure acceleration. It is usually composed of masses, dampers, elastic components, sensitive components, and adaptive circuits. In the process of acceleration, the sensor obtains the acceleration value by using Newton's second law by measuring the inertial force on the mass block.
According to the different sensitive components of the sensor, common acceleration sensors include capacitive, inductive, strain-type, piezoresistive, piezoelectric and so on.
CVBS interface: CVBS Chinese name is composite synchronous video broadcast signal or composite video blanking and synchronization. CVBS is a widely used standard, also called baseband video or RCA video. It is the traditional image data transmission method of the (US) National Television Standards Committee (NTSC) television signal. It transmits data in analog waveforms.
Composite video contains color difference (hue and saturation) and brightness (brightness) information, and they are synchronized in the blanking pulse and transmitted with the same signal. It is a format before an analog TV program (image) signal is combined with a sound signal and modulated to a radio frequency carrier. In fast scanning NTSC televisions, the very high frequency (VHF) or ultra high frequency (UHF) carrier is the modulation amplitude used in composite video, and the signal generated at this time is approximately 6 MHz wide. Some closed-circuit television systems use coaxial cables to transmit composite video at short distances. Some DVD players and video tape recorders (VCR) provide composite video input and output through a pickup socket, which is also called an RCA connector. In composite video, the interference of color difference and brightness information is inevitable, especially when the signal is weak. This is why NTFS TV stations that use VHF or UHF at long distances use old whip antennas. "Rabbit ears", or outdoor "air" often contain false or shaking colors. CVBS is an older display method, more accurately the first generation video display output method (the second generation is S-VIDEO, the third generation is VGA, the fourth generation is DVI, and the fifth generation is HDMI).
HDMI interface: High Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a fully digital video and sound transmission interface that can transmit uncompressed audio and video signals. HDMI can be used for set-top boxes, DVD players, personal computers, televisions, game consoles, integrated amplifiers, digital audio and televisions and other equipment. HDMI can send audio and video signals at the same time. As the audio and video signals use the same wire, the installation difficulty of the system line is greatly simplified.
RS232 interface: The RS-232 interface complies with the serial data communication interface standard established by the Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA). The original number is EIA-RS-232 (referred to as 232, RS232). It is widely used for computer serial interface peripheral connection, connecting cables and machinery, electrical characteristics, signal functions and transmission processes.
In short: a 25-core interface standard developed by EIA, also known as EIA-232.
RS485 interface: Smart meters have developed with the maturity of single-chip technology in the early 1980s. The world meter market is basically monopolized by smart meters. This is due to the needs of enterprise informatization, and one of the necessary conditions for enterprises in meter selection is It must have a networked communication interface. At first, it was a simple process quantity of data analog signal output.
Later, the instrument interface was an RS232 interface. This interface can realize point-to-point communication, but this method cannot realize the networking function. The subsequent RS485 solves this problem. RS-485 is also known as TIA-485-A, ANSI/TIA/EIA-485 or TIA/EIA-485. RS485 is a standard that defines the electrical characteristics of drivers and receivers in a balanced digital multipoint system. The standard is defined by the Telecommunications Industry Association and the Electronics Industry Alliance. Digital communication networks using this standard can effectively transmit signals under long-distance conditions and in environments with high electronic noise. RS-485 makes it possible to connect to the local network and the configuration of multi-branch communication links. RS485 has two-wire and four-wire connections. The four-wire system can only achieve point-to-point communication. It is rarely used now. The two-wire connection method is mostly used. This wiring method is a bus topology. Up to 32 nodes can be connected to the same bus.
In the RS485 communication network, a master-slave communication method is generally adopted, that is, a master with multiple slaves. In many cases, when connecting the RS-485 communication link, simply use a pair of twisted pair to connect the "A" and "B" ends of each interface, and ignore the signal ground connection. This connection method is used in many The occasion can work normally, but it has buried a lot of hidden dangers.
Reason 1 is common mode interference: The RS-485 interface adopts differential signal transmission mode, and does not need to detect the signal relative to a certain reference point. The system only needs to detect the potential difference between the two wires, but it is easy to overlook that the transceiver has a certain common mode Voltage range, the common mode voltage range of RS-485 transceiver is -7 to +12V.
Only when the above conditions are met, the entire network can work normally; When the common mode voltage in the network line exceeds this range, it will affect the stability and reliability of the communication, and even damage the interface; the second reason is the problem of EMI: the common mode part of the output signal of the driver needs a return path, such as no low resistance return The channel (signal ground) will return to the source in the form of radiation, and the entire bus will radiate electromagnetic waves outward like a huge antenna.
In short: A 25-core interface standard developed by EIA has also become EIA-485.
USB3.0 interface: USB 3.0 is a new generation of USB interface. It is characterized by a very fast transmission rate, which can theoretically reach 5Gbps, which is 10 times faster than the common 480Mbps High Speed USB (referred to as USB 2.0) and fully surpasses IEEE 1394 and eSATA. The appearance is basically the same as the ordinary USB interface, and it is compatible with USB 2.0 and USB 1.1 devices. USB 3.0 is the latest USB specification, which was initiated by large companies such as Intel. USB 2.0 has been generally recognized by PC manufacturers, and the interface has become a must-have for hardware manufacturers. Just look at the motherboards commonly used at home. On November 17, 2008, the USB 3.0 standard was officially completed and publicly released.
HDD: HDD, the abbreviation of Hard Disk Drive, is the English name of the hard disk drive. The most basic computer memory, the computer hard disk C drive and D drive that we often say in our computer are disk partitions, which belong to the hard disk drive. The common disk capacity of hard disk is 80G, 128G, 160G, 256G, 320G, 500G, 750G, 1TB, 2TB and so on. Hard disks can be divided into 3.5-inch, 2.5-inch, 1.8-inch, etc. according to the size; according to the number of revolutions, they can be divided into 5400rpm/7200rpm/10000rpm, etc.; according to the interface can be divided into PATA, SATA, SCSI, etc. PATA and SATA are generally desktop applications with large capacity and relatively low price, suitable for home use; while SCSI is generally high-end applications such as servers and workstations, with relatively small capacity and more expensive, but with better performance and higher stability.
Video footage (Video Footage): footage, an English word, is mainly used as a noun, and used as a noun to be translated as "to calculate the length by the ruler; the number of the ruler; the continuous shot". Video Footage means a video clip. The length of the video clip can be set in the host (car video recorder) menu according to customer needs: 3 seconds, 5 seconds, 10 seconds, 15 seconds, 1 minute, 2 minutes, 5 minutes, 10 Minutes, 30 minutes can be set.
Front-facing camera: Front-facing camera, a camera that records the road conditions in front of the vehicle or the incident.
Reversing camera: Reversing Camera, that is for the camera with mirroring function for reversing or parking. When the vehicle is reversing, it can automatically switch to the reversing mode to record videos.
PTZ camera: PTZ camera. PTZ: In the security monitoring application, it is the abbreviation of Pan/Tilt/Zoom, which represents the omni-directional (left-right/up-down) movement of the pan/tilt and the lens zoom and zoom control.
ADAS camera: Advanced Driving Assistance System (Advanced Driving Assistance System) uses a variety of sensors (millimeter wave radar, lidar, mono/binocular cameras and satellite navigation) installed in the car to come at any time while the car is driving, sensing the surrounding environment, collecting data, identifying, detecting and tracking static and dynamic objects, and combining with navigation map data to perform system calculation and analysis, so as to allow drivers to perceive possible dangers in advance, effectively increasing car driving's comfort and safety. In recent years, the ADAS market has grown rapidly. This type of system was originally limited to the high-end market, but is now entering the mid-range market. At the same time, many low-tech applications are more common in the entry-level passenger car field, and improved new sensor technologies are also available, creating new opportunities and strategies for system deployment.
As far as the vehicle monitoring industry is concerned, the ADAS camera refers to a camera with LDWS (Lane Departure Warning System) function, anti-front collision and anti-rear collision warning functions.
DSM camera: Full name Driver's Status Monitoring, that is, driver's status monitoring camera, built-in driver's facial recognition chip and algorithm, can detect the driving process of the vehicle, the status of the driver (such as sleeping, blinking, turning head, yawning, smoking, etc.) Face disappears, phone calls, etc.) of the camera.
Vehicle-mounted explosion-proof camera: explosion-proof camera is an explosion-proof monitoring product, which is a cross product of the explosion-proof industry and the monitoring industry. Because conventional camera products cannot be used in high-risk flammable and explosive scenes, they need to have explosion-proof functions and have relevant issues issued by national authorities. Only certified products can be called explosion-proof cameras. The explosion-proof camera that can be installed on the vehicle is called: the vehicle-mounted explosion-proof camera.
People counting camera: A camera installed on the car to count the flow and number of passengers. Passenger flow statistics server The passenger flow statistics server is based on video image recognition technology, which can identify and extract the head features in a set area in the image, and count the number of heads (that is, the number of people). The passenger flow statistics server is responsible for analyzing the input video stream, and through the system configuration, setting the people counting area and the direction of entry and exit, etc., calculates the data such as the number of people entering and exiting the channel or the designated area.
Various optional car accessories, car externally-connected devices and car sensors: host (vehicle-mounted mobile dvr)'s hard disk box, hard disk card reader, car display, fireproof box, car power supply, LED controller, car backup power supply, car router, car LED display, voice pickup device, fuel consumption sensor, rain sensor, door switch sensor, emergency alarm button (Panic Button), tire pressure monitor, speed sensor, acceleration sensor and brake sensor, etc.
The terminologies of the servers used in vehicle monitoring platform:
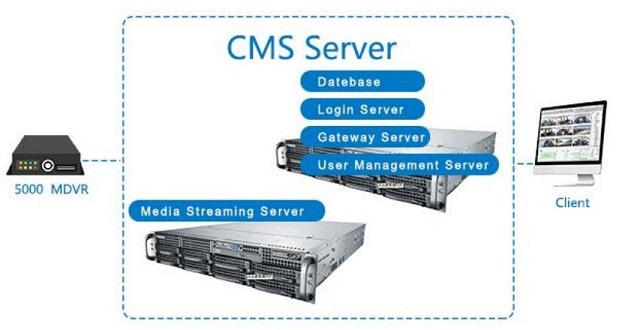
1. CMS server: CMS is the abbreviation of Content Management System, meaning "content management system". Content management system is the new favorite of enterprise information construction and e-government, and it is also a relatively new market. For content management, the industry does not have a unified definition, and different organizations have different understandings. In the vehicle monitoring industry, CMS server refers to the data management server (mainly video stream data, GPS data and various alarm data).
2. Login server: Login Server, a server dedicated to recording and storing user login data.
3. Web server: Web Server, a server dedicated to recording and storing the data required and generated by the user to access the web page version of the monitoring platform.
4. DAS server: Direct-Attached Storage Sever, open system direct-attached storage server, namely: Open system direct-attached storage (Direct-Attached Storage, DAS for short) has a history of nearly forty years. With the continuous growth of data, especially when it is more than hundreds of GB, its problems in backup, recovery, expansion, disaster recovery, etc. have become increasingly troublesome for system administrators. The connection channel between the direct-attached storage and the server host usually adopts SCSI connection. As the processing power of the server CPU becomes stronger and stronger, the storage hard disk space becomes larger and larger, and the number of hard disks in the array increases. Become an IO bottleneck; the server host SCSI ID resources are limited, and the SCSI channel connections that can be established are limited.
5. DMS server: Device Management Server, device management server.
6. ARS server: Actively Registering Server: Actively Registering Server, which can also be called Initiative Server, which is used by the device to actively register to the server on the server side.
7. SS server: namely Storage Service Server, data storage server.
8. MTS server: Media Transferring Service Server, streaming media server, can also be called Streaming Media Server.
9. Gateway server: Gateway Server. A server dedicated to managing and configuring all gateways and interfaces.
10. User Management Server: User Management Server, a server dedicated to managing user data.
11. Database server: Database Sever, a database server, a server dedicated to managing databases (such as MySQL).
12. Other servers: Other Servers.
Topological graph of Platform 1:
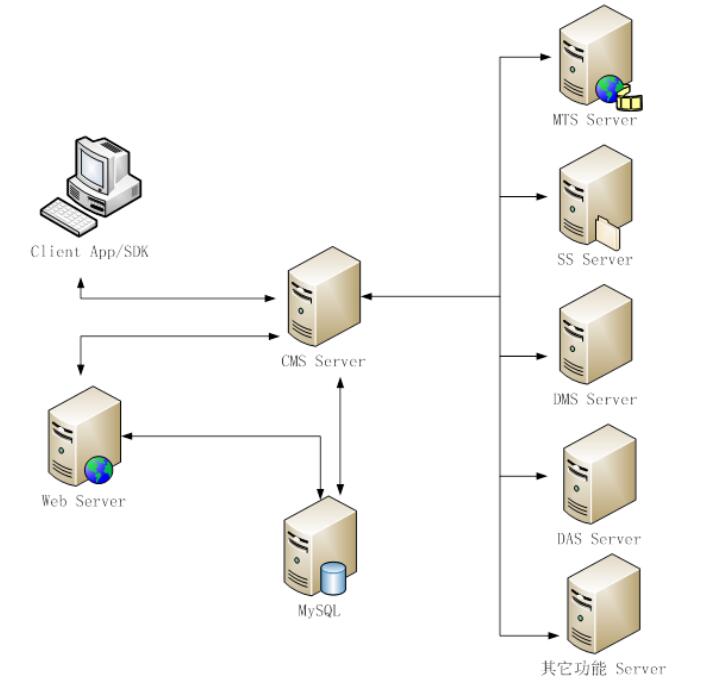 Topological graph of Platform 2 (Type A):
Topological graph of Platform 2 (Type A):
Topological graph of Platform 2 (Type B):

Other terminologies in the industry of vehicle and fleet surveillance:
ECU: ECU (Electronic Control Unit) electronic control unit, also known as "travel computer", "vehicle computer" and so on. It is the same as an ordinary computer, consisting of a microcontroller (MCU), memory (ROM, RAM), input/output interface (I/O), analog-to-digital converter (A/D), and large-scale integrated circuits such as shaping and driving. composition. In a simple sentence, "ECU is the brain of the car".
4CIF: 4 times common intermediate format, a color image format, 704×576 images (for PAL color images)
BNC: Full name Bayonet Nut Connector, a connector for coaxial cable
CIF: Common Intermediate Format, a color image format, 352×288 pixels (for PAL color images)
DHCP: Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol, used to dynamically assign configuration information
DNS: Domain Name System, which converts names to IP addresses in a user-friendly way
EIA: Electronics Industry Association, a standard body
H.264: A video compression standard, also known as MPEG-4 (PART10)
HTTP: Hypertext Transfer Protocol
IDE: A type of disk drive interface
IP: Internet Protocol
ISO: International Organization for Standardization, a standard system
ITU-T: International Telecommunication Union-Telecommunications Standards Department
NFS: Network File System
NTSC: a television system
PAL: A television system
PPP: Point to Point Protocol
PPPoE: Transmission of PPP protocol on Ethernet
QCIF: Quarter Common Intermediate Format
RCA: A video and audio interface (commonly known as lotus head)
RTP: Real-time Transport Protocol
SDK: Software Development Kit
API: Application development interface
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol
UDP: User Datagram Protocol
URL: Uniform Resource Locator
USB: Universal Serial Bus
UTP: Unshielded twisted pair, this book refers to the Ethernet interface
VGA: Represents a resolution, 640×480 pixels. This article refers to a kind of display, the display resolution can support 800×600/60HZ, 800×600/75HZ, 1024×768/60HZ
HD: stands for a resolution, an image or video with a vertical resolution greater than or equal to 720, also known as high-definition image or high-definition video, and the size is generally 1280×720 and 1920×1080. The full name of "HD" is "High Definition".
4K: represents a resolution, 4K resolution belongs to ultra-high-definition resolution. At this resolution, the audience will be able to see every detail and every close-up in the picture. If the cinema adopts 4096×2160 resolution, no matter where in the cinema, the audience can clearly see every detail of the picture.
4K resolution means that the pixel value of each line in the horizontal direction reaches or approaches 4096, regardless of the aspect ratio. Depending on the scope of use, 4K resolution also has a variety of derivative resolutions, such as, Full Aperture 4K's 4096×3112, Academy 4K's 3656×2664 and UHDTV standard 3840×2160, etc., all belong to 4K resolution. category.



